 Overview
OverviewWhat Is A hammertoe? A hammer toe, or claw toe, describes a condition where the toe(s) become buckled, contracted or crooked. The toe could even cross over an adjacent toe, which is called a cross over toe. Any of the toes may be affected, but the 2nd and 5th toe are most commonly involved.
Causes
A hammertoe is formed due an abnormal balance of the muscles in the toes. This abnormal balance causes increased pressures on the tendons and joints of the toe, leading to its contracture. Heredity and trauma can also lead to the formation of a hammertoe. Arthritis is another factor, because the balance around the toe in people with arthritis is so disrupted that a hammertoe may develop. Wearing shoes that are too tight and cause the toes to squeeze can also be a cause for a hammertoe to form.
 Symptoms
SymptomsThe symptoms of hammertoe are progressive, meaning that they get worse over time. Hammertoe causes the middle joint on the second, third, fourth, or fifth toes to bend. The affected toe may be painful or irritated, especially when you wear shoes. Areas of thickened skin (corns) may develop between, on top of, or at the end of your toes. Thickened skin (calluses) may also appear on the bottom of your toe or the ball of your foot. It may be difficult to find a pair of shoes that is comfortable to wear.
Diagnosis
Although hammertoes are readily apparent, to arrive at a diagnosis the foot and ankle surgeon will obtain a thorough hammertoe history of your symptoms and examine your foot. During the physical examination, the doctor may attempt to reproduce your symptoms by manipulating your foot and will study the contractures of the toes. In addition, the foot and ankle surgeon may take x-rays to determine the degree of the deformities and assess any changes that may have occurred.
Non Surgical Treatment
You can usually use over-the-counter cushions, pads, or medications to treat bunions and corns. However, if they are painful or if they have caused your toes to become deformed, your doctor may opt to surgically remove them. If you have blisters on your toes, do not pop them. Popping blisters can cause pain and infection. Use over-the-counter creams and cushions to relieve pain and keep blisters from rubbing against the inside of your shoes. Gently stretching your toes can also help relieve pain and reposition the affected toe.
Surgical Treatment
If this fails or if treatment is not sought until the toes are permanently misaligned, then surgery may be required. Surgery may involve either cutting the tendon or fusing the joint. Congenital conditions should be treated in early childhood with manipulations and splinting.
 A bunion (a.k.a Hallux Valgus) is a common foot condition associated with a prominent bump on the inside of the forefoot (see Figure 1). The word bunion? comes from the Greek root for the word turnip. Bunions can lead to discomfort over the prominence, especially if patients wear tight fitting shoes. It is common for bunions to run in family? and gradually increase over time. The vast majority of bunions can be managed successfully with basic non-operative treatment. Surgery is reserved for patients who have persistent symptoms in spite of appropriate non-operative treatment.
A bunion (a.k.a Hallux Valgus) is a common foot condition associated with a prominent bump on the inside of the forefoot (see Figure 1). The word bunion? comes from the Greek root for the word turnip. Bunions can lead to discomfort over the prominence, especially if patients wear tight fitting shoes. It is common for bunions to run in family? and gradually increase over time. The vast majority of bunions can be managed successfully with basic non-operative treatment. Surgery is reserved for patients who have persistent symptoms in spite of appropriate non-operative treatment.


 The Achilles tendon is a conjoined tendon composed of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles with occasional contribution from the plantaris muscle, and it inserts on the calcaneal tuberosity. The plantaris muscle is absent in 6% to 8% of individuals. The Achilles tendon is approximately 15-cm long and is the largest and strongest tendon in the human body. The tendon spirals approximately 90? from its origin to its insertion and this twisting produces an area of stress approximately 2- to 5-cm proximal to its insertion. The tendon has no true synovial sheath; instead it is wrapped in a paratenon. The Achilles tendon experiences the highest loads of any tendon in the body, and bears tensile loads up to 10 times body weight during athletic activities. The tendon most commonly ruptures in a region 2- to 6-cm proximal to its insertion. Causes The Achilles tendon is a strong bands of fibrous connective tissue that attaches the calf muscle to the heel bone. When the muscle contracts, the tendon transmits the power of this contraction to the heel bone, producing movement. The Achilles tendon ruptures because the load applied to it is greater than the tendon's ability to withstand that load. This usually occurs as a result of a sudden, quick movement where there is a forceful stretch of the tendon or a contraction of the muscles eg: jumping, sprinting, or pushing off to serve in tennis. This occurs most often in sports that require a lot of stopping and starting (acceleration-deceleration sports) such as tennis, basketball, netball and squash. The Achilles tendon is on average 15cm in length. Most ruptures occur 2-6cm above where the tendon inserts into the heel bone. This is the narrowest portion of the Achilles tendon and is also the area with the poorest blood supply. achilles tendon rupture is most common when the muscles and tendon have not been adequately stretched and warmed up prior to exercise, or when the muscles are fatigued. the Achilles tendon has a poor blood supply, which makes it susceptible to injury and slow to heal after injury. During exercise the amount of blood able to travel to the tendon is decreased, further increasing the risk of rupture. Most experts agree that there are no warning signs of an impending rupture. However, frequent episodes of Achilles tendonitis (tendon inflammation) can weaken the tendon and make it more susceptible to rupture. Symptoms Symptoms usually come on gradually. Depending on the severity of the injury, they can include Achilles pain, which increases with specific activity, with local tenderness to touch. A sensation that the tendon is grating or cracking when moved. Swelling, heat or redness around the area. The affected tendon area may appear thicker in comparison to the unaffected side. There may be weakness when trying to push up on to the toes. The tendon can feel very stiff first thing in the morning (care should be taken when getting out of bed and when making the first few steps around the house). A distinct gap in the line of the tendon (partial tear). Diagnosis A consultation and physical exam with a qualified musculoskeletal expert is the first step. X-ray or MRI scanning may be required for a diagnosis. Once a rupture is diagnosed it should be treated to prevent loss of strength and inadequate healing. Non Surgical Treatment Achilles tendon ruptures can be treated non-operatively or operatively. Both of these treatment approaches have advantages and disadvantages. In general, younger patients with no medical problems may tend to do better with operative treatment, whereas patients with significant medical problems or older age may be best served with non-operative treatment. However, the decision of how the Achilles tendon rupture is treated should be based on each individual patient after the advantages and disadvantages of both treatment options are reviewed. It is important to realize that while Achilles tendon ruptures can be treated either non-operatively or operatively, they must be treated. A neglected Achilles tendon rupture (i.e. one where the tendon ends are not kept opposed) will lead to marked problems of the leg in walking, which may eventually lead to other limb and joint problems. Furthermore, late reconstruction of non-treated Achilles tendon rupture is significantly more complex than timely treatment.
The Achilles tendon is a conjoined tendon composed of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles with occasional contribution from the plantaris muscle, and it inserts on the calcaneal tuberosity. The plantaris muscle is absent in 6% to 8% of individuals. The Achilles tendon is approximately 15-cm long and is the largest and strongest tendon in the human body. The tendon spirals approximately 90? from its origin to its insertion and this twisting produces an area of stress approximately 2- to 5-cm proximal to its insertion. The tendon has no true synovial sheath; instead it is wrapped in a paratenon. The Achilles tendon experiences the highest loads of any tendon in the body, and bears tensile loads up to 10 times body weight during athletic activities. The tendon most commonly ruptures in a region 2- to 6-cm proximal to its insertion. Causes The Achilles tendon is a strong bands of fibrous connective tissue that attaches the calf muscle to the heel bone. When the muscle contracts, the tendon transmits the power of this contraction to the heel bone, producing movement. The Achilles tendon ruptures because the load applied to it is greater than the tendon's ability to withstand that load. This usually occurs as a result of a sudden, quick movement where there is a forceful stretch of the tendon or a contraction of the muscles eg: jumping, sprinting, or pushing off to serve in tennis. This occurs most often in sports that require a lot of stopping and starting (acceleration-deceleration sports) such as tennis, basketball, netball and squash. The Achilles tendon is on average 15cm in length. Most ruptures occur 2-6cm above where the tendon inserts into the heel bone. This is the narrowest portion of the Achilles tendon and is also the area with the poorest blood supply. achilles tendon rupture is most common when the muscles and tendon have not been adequately stretched and warmed up prior to exercise, or when the muscles are fatigued. the Achilles tendon has a poor blood supply, which makes it susceptible to injury and slow to heal after injury. During exercise the amount of blood able to travel to the tendon is decreased, further increasing the risk of rupture. Most experts agree that there are no warning signs of an impending rupture. However, frequent episodes of Achilles tendonitis (tendon inflammation) can weaken the tendon and make it more susceptible to rupture. Symptoms Symptoms usually come on gradually. Depending on the severity of the injury, they can include Achilles pain, which increases with specific activity, with local tenderness to touch. A sensation that the tendon is grating or cracking when moved. Swelling, heat or redness around the area. The affected tendon area may appear thicker in comparison to the unaffected side. There may be weakness when trying to push up on to the toes. The tendon can feel very stiff first thing in the morning (care should be taken when getting out of bed and when making the first few steps around the house). A distinct gap in the line of the tendon (partial tear). Diagnosis A consultation and physical exam with a qualified musculoskeletal expert is the first step. X-ray or MRI scanning may be required for a diagnosis. Once a rupture is diagnosed it should be treated to prevent loss of strength and inadequate healing. Non Surgical Treatment Achilles tendon ruptures can be treated non-operatively or operatively. Both of these treatment approaches have advantages and disadvantages. In general, younger patients with no medical problems may tend to do better with operative treatment, whereas patients with significant medical problems or older age may be best served with non-operative treatment. However, the decision of how the Achilles tendon rupture is treated should be based on each individual patient after the advantages and disadvantages of both treatment options are reviewed. It is important to realize that while Achilles tendon ruptures can be treated either non-operatively or operatively, they must be treated. A neglected Achilles tendon rupture (i.e. one where the tendon ends are not kept opposed) will lead to marked problems of the leg in walking, which may eventually lead to other limb and joint problems. Furthermore, late reconstruction of non-treated Achilles tendon rupture is significantly more complex than timely treatment.  Surgical Treatment Thanks to a new surgical technique, operative procedures are often more beneficial.The operative treatment of Achilles tendon ruptures has significantly changed in recent years. The objective today is to connect the torn tendons using modern suture and possibly adhesive materials. Through small surgical incisions the ends of the torn tendon are surgically exposed, and sutures are used to tie the ends permanently together. Thus, the operated repaired tendon is again resilient within a reasonable time. The cast treatment and walking on crutches required in the past, is with this procedure usually not necessary. Instead, functional treatment following the surgery involves wearing a special boot, meaning that the patient can put weight onto the operated leg again within a few days after surgery. Physical therapy training will start immediately following the operation. The philosophy behind such an early functional treatment is that tissue adequately adapts to stress and thus accelerates the healing process. For the patient, the modern surgical treatment of an Achilles tendon rupture has the distinct advantage that no prolonged hospital stay is necessary. Hospital stay usually lasts only a few days. Using crutches, patients can return to work soon after the surgery. Prevention Achilles tendon rupture can be prevented by avoiding chronic injury to the Achilles tendon (i.e. tendonitis), as well as being careful to warm up and stretch properly before physical activity. Additionally, be sure to use properly fitting equipment (e.g. running shoes) and correct training techniques to avoid this problem!
Surgical Treatment Thanks to a new surgical technique, operative procedures are often more beneficial.The operative treatment of Achilles tendon ruptures has significantly changed in recent years. The objective today is to connect the torn tendons using modern suture and possibly adhesive materials. Through small surgical incisions the ends of the torn tendon are surgically exposed, and sutures are used to tie the ends permanently together. Thus, the operated repaired tendon is again resilient within a reasonable time. The cast treatment and walking on crutches required in the past, is with this procedure usually not necessary. Instead, functional treatment following the surgery involves wearing a special boot, meaning that the patient can put weight onto the operated leg again within a few days after surgery. Physical therapy training will start immediately following the operation. The philosophy behind such an early functional treatment is that tissue adequately adapts to stress and thus accelerates the healing process. For the patient, the modern surgical treatment of an Achilles tendon rupture has the distinct advantage that no prolonged hospital stay is necessary. Hospital stay usually lasts only a few days. Using crutches, patients can return to work soon after the surgery. Prevention Achilles tendon rupture can be prevented by avoiding chronic injury to the Achilles tendon (i.e. tendonitis), as well as being careful to warm up and stretch properly before physical activity. Additionally, be sure to use properly fitting equipment (e.g. running shoes) and correct training techniques to avoid this problem!


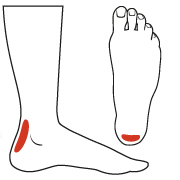 An Achilles tendon rupture is when part or all of your tendon is torn. The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle in your lower leg to your heel bone. It allows you to point your foot down and to rise on your toes. A tear is caused by an injury or increased pressure, such as during sports or a fall. The following may make your Achilles tendon weak or stiff, and more likely to tear. A past tendon tear. Lack of physical activity. Abnormal bone structure in your foot. Obesity. Older age. Medicines, such as steroids and antibiotics.
An Achilles tendon rupture is when part or all of your tendon is torn. The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle in your lower leg to your heel bone. It allows you to point your foot down and to rise on your toes. A tear is caused by an injury or increased pressure, such as during sports or a fall. The following may make your Achilles tendon weak or stiff, and more likely to tear. A past tendon tear. Lack of physical activity. Abnormal bone structure in your foot. Obesity. Older age. Medicines, such as steroids and antibiotics.
